Micromotor Innovations and Brazilian Fertility Industry Regulatory Frameworks

Introduction
The realm of assisted reproductive technology (ART) has seen remarkable breakthroughs over the past decades, with nanotechnology emerging as a frontier capable of reshaping how infertility is treated. A compelling innovation in this field is the use of sperm-carrying micromotors, as detailed in Cellular Cargo Delivery: Toward Assisted Fertilization by Sperm-Carrying Micromotors. This revolutionary technology offers a precise method for transporting immotile sperm to oocytes, providing a novel solution to severe male infertility challenges. Such innovations bring into focus the need for comprehensive legislation and regulatory systems to ensure their safe and ethical integration. Brazil, a global leader in ART, boasts a robust legislative and regulatory framework under RDC No. 771/2022 and RDC No. 81/2008, overseen by ANVISA, the National Health Surveillance Agency. This analysis delves into the history, regulation, sector-specific practices, market dynamics, and scientific implications of ART in Brazil while exploring the integration of micromotor technology into the country’s ecosystem.

Brazilian History and Legislation in Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
The evolution of assisted reproductive technology in Brazil reflects a rich history of scientific progress and ethical deliberation. From the pioneering days of IVF in the 1980s to the current regulatory frameworks shaped by RDC No. 81/2008 and RDC No. 771/2022, Brazil has laid a solid foundation for innovation in reproductive medicine. This history not only highlights the country’s commitment to advancing fertility treatments but also provides the groundwork for integrating technologies like sperm-carrying micromotors.
Historical Context
Since its inception in the 1980s, ART in Brazil has evolved from rudimentary in vitro fertilization (IVF) techniques to a wide array of sophisticated treatments, including cryopreservation, preimplantation genetic testing, and egg donation programs. The growth of this sector reflects not only advancements in technology but also Brazil’s commitment to providing equitable access to fertility treatments. Public health policies, coupled with private sector innovations, have driven significant developments in ART infrastructure.
Legislative Milestones
- RDC No. 81/2008:
- Regulates the importation of biological materials for therapeutic use, ensuring that only approved entities handle such sensitive materials.
- Stipulates traceability requirements via systems like SISCOMEX, maintaining transparency and safety throughout the supply chain.
- Mandates adherence to biosafety standards to mitigate risks associated with international transfers of biological materials.
- RDC No. 771/2022:
- Focuses on good practices for germinative cells and embryos, emphasizing safety, quality, and the ethical management of ART materials.
- Introduces advanced requirements for traceability and the documentation of donors, reinforcing compliance with both national and international standards.
- Law No. 9782/1999:
- Establishes ANVISA’s role in regulating ART practices, conferring authority to oversee the importation, licensing, and monitoring of ART-related entities.
- Ethical Guidelines:
- Enforced by the Federal Council of Medicine (CFM), these guidelines prohibit unethical practices, such as cloning or the commercialization of gametes, and emphasize the importance of donor anonymity.
The Path Forward
Brazil’s legislative framework balances innovation and ethics, ensuring ART advances align with societal values. This comprehensive approach positions Brazil as a promising destination for integrating technologies like sperm-carrying micromotors.
Brazil’s legislative journey in assisted reproductive technology underscores the nation’s dedication to ethical innovation and patient safety. By balancing progressive policies with rigorous regulatory oversight, Brazil has created an environment conducive to groundbreaking advancements. This strong foundation positions the country as a leader in adopting cutting-edge technologies like micromotors, ensuring they align with societal values and clinical needs.

Current Regulation and Regulatory Agencies
ANVISA’s Role in ART
The regulatory framework governing assisted reproductive technology in Brazil is both comprehensive and adaptive, ensuring safety, ethics, and efficacy in fertility treatments. Spearheaded by ANVISA and supported by state and municipal health authorities, these regulations, including RDC No. 81/2008 and RDC No. 771/2022, provide a robust foundation for innovation. They also set the stage for integrating advanced solutions, such as micromotors, into clinical practice.
ANVISA’s Responsibilities
- Import Approvals:
- Evaluates extensive documentation, including donor health certifications and transport protocols, before approving biological material imports.
- Facility Inspections:
- Conducts rigorous inspections to verify compliance with RDC No. 771/2022, particularly concerning infrastructure and storage standards.
- Monitoring and Traceability:
- Leverages digital tools to track the movement and use of reproductive materials, safeguarding against misuse or unethical practices.
Local Oversight
State and municipal health authorities collaborate with ANVISA, ensuring localized enforcement of ART regulations. These entities are critical in overseeing the licensing and operational standards of clinics.
Compliance Requirements
- Use of validated transportation systems for cryopreserved materials.
- Adherence to donor anonymity and other ethical safeguards.
- Regular auditing of international sperm and egg banks supplying materials to Brazil.
Brazil’s regulatory oversight in assisted reproductive technology demonstrates the effectiveness of comprehensive governance in fostering safe and ethical practices. By maintaining alignment with international standards and adapting to emerging technologies, Brazil ensures its ART sector remains at the forefront of innovation. This dynamic regulatory ecosystem not only safeguards patient welfare but also promotes the seamless integration of new advancements like micromotors.

Best Practices in ART
Sector-Specific Guidelines
Establishing best practices in assisted reproductive technology is essential for ensuring safe and effective fertility treatments. In Brazil, a combination of legislative mandates and professional guidelines shapes the sector, emphasizing ethical considerations, technical precision, and patient safety. These best practices align with global standards while addressing local needs, paving the way for innovations like micromotor-assisted fertilization.
Procurement and Transport
- Imported materials must comply with RDC No. 81/2008 and RDC No. 771/2022, ensuring proper documentation and storage protocols.
- Transport requires the use of cryopreservation containers or dry shippers to maintain the viability of gametes and embryos.
Facility Standards
- ART clinics must meet stringent criteria, including the use of cleanroom environments and validated diagnostic tools.
- Regular inspections ensure compliance with established best practices and adherence to ethical standards.
Ethical Practices
- Commercialization of human gametes is strictly prohibited.
- Clinics must uphold donor anonymity, aligning with ethical and legal frameworks.
Brazil’s adherence to best practices in assisted reproductive technology ensures the highest standards of safety, ethics, and efficiency. These protocols prepare the sector for the adoption of transformative technologies like micromotors, enhancing patient care and reinforcing Brazil’s reputation as a global leader in reproductive medicine. The integration of such innovations demonstrates the sector’s capacity to adapt while maintaining its commitment to quality and ethical integrity.

Brazil’s Current Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Market
Thriving Demand for ART
The growing demand for assisted reproductive technology in Brazil underscores the sector’s vast market potential. With over 400 specialized clinics and thousands of procedures conducted annually, Brazil’s ART market is a regional leader. This thriving environment provides fertile ground for incorporating innovative technologies like micromotors, which promise to revolutionize the treatment landscape and address unmet needs in fertility care.
Market Overview
Brazil’s ART market is robust, with over 400 specialized clinics catering to thousands of patients annually. Key indicators of market activity include:
- Clinics like Semear Fertilidade, which reported over 54,000 frozen embryos in storage in 2024, demonstrating the scale and efficiency of ART services.
- The high demand for services such as egg freezing, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and oocyte donation, highlighting opportunities for growth and innovation.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Regional disparities limit access to ART services in rural areas.
- High treatment costs restrict ART to wealthier demographics.
Opportunities:
- Increasing investments in ART infrastructure and technology.
- Integration of innovations like sperm-carrying micromotors, which could attract both local and international clientele.
Brazil’s ART market combines robust growth, advanced infrastructure, and ethical practices, creating an ideal environment for adopting innovations in assisted reproductive technology. While challenges like cost and accessibility persist, the sector’s strengths offer a pathway to overcoming these barriers. Integrating technologies like micromotors could further elevate Brazil’s position as a leader in reproductive medicine, unlocking new opportunities for patients and providers alike.
Scientific Overlay and Curiosities: Sperm-Carrying Micromotors
Revolutionary Advances in ART
At the cutting edge of assisted reproductive technology lies the revolutionary innovation of sperm-carrying micromotors. These devices, capable of transporting immotile sperm to oocytes with unprecedented precision, represent a significant breakthrough in addressing male infertility. By aligning this technology with Brazil’s advanced ART framework, the country can redefine the future of reproductive medicine.
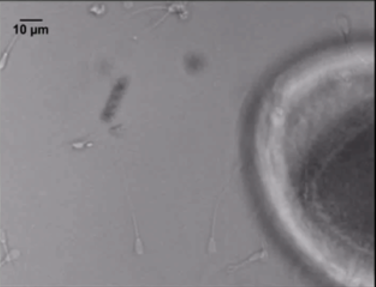
Revolutionary Potential
Sperm-carrying micromotors, as detailed in the study, present a breakthrough in addressing male infertility. Key features include:
- Precision Transport: These micromotors can carry immotile sperm directly to oocytes, reducing the invasiveness of procedures.
- Biocompatible Materials: The metal-coated polymer microhelices ensure safety and reliability under physiological conditions.
Challenges and Future Directions
Challenges:
- Biocompatibility and scalability need refinement.
- Ethical considerations regarding clinical applications.
Future Directions:
- Broader clinical trials to validate efficacy.
- Potential to replace more invasive techniques like ICSI.

Sperm-carrying micromotors symbolize a transformative step in assisted reproductive technology, blending nanotechnology with clinical expertise to address male infertility. Their potential integration into Brazil’s ART ecosystem highlights the sector’s adaptability and innovation-driven approach. By bridging scientific advancements with regulatory compliance, Brazil can lead the charge in revolutionizing reproductive medicine.

Legislative and Regulatory Implications for Micromotor Integration
Adapting Regulations for Innovation
Integrating groundbreaking solutions like micromotors into Brazil’s assisted reproductive technology sector requires navigating a robust regulatory landscape. Laws such as RDC No. 771/2022 provide a solid foundation for safety and ethical compliance but also demand careful adaptation to accommodate emerging technologies. This process underscores the importance of aligning innovation with established legal and ethical standards.
Regulatory Adjustments
To integrate micromotor technology, Brazil must:
- Develop preclinical trial requirements for nanotechnology in ART.
- Expand traceability protocols to include micromotor-based systems.
- Address ethical implications, ensuring patient safety and compliance with donor-related guidelines.
Compliance Strategies
- Collaborate with international bodies to harmonize standards.
- Train ART professionals in the use of micromotor technologies.
Navigating Brazil’s regulatory framework for assisted reproductive technology is both a challenge and an opportunity. By adapting its comprehensive laws to include advancements like micromotors, Brazil can maintain its commitment to safety and ethics while fostering innovation. This collaborative effort between regulators, clinicians, and innovators will solidify Brazil’s position as a global leader in reproductive medicine.

Final Insights and Opportunities in Assisted Reproductive Technology
The integration of assisted reproductive technology innovations, such as sperm-carrying micromotors, into Brazil’s thriving ART sector illustrates the dynamic intersection of scientific breakthroughs, ethical commitments, and regulatory rigor. Brazil’s robust legislative foundation, highlighted by RDC No. 81/2008 and RDC No. 771/2022, establishes a framework that prioritizes safety, ethical standards, and technological adaptability. These elements, overseen by ANVISA and supported by local health authorities, ensure a balance between fostering innovation and protecting patient welfare.
While navigating the complexities of compliance with these stringent laws may initially appear challenging, they ultimately create a structured environment conducive to integrating transformative technologies. Innovations like micromotors, which address critical infertility issues with unprecedented precision, exemplify the potential of aligning scientific advancements with Brazil’s robust regulatory ecosystem. The country’s market dynamics—characterized by a high demand for fertility treatments, advanced clinical infrastructure, and a growing focus on cutting-edge solutions—present an opportunity for global innovators to enter and thrive in this space.
Hegemoni Regulatory & Business Solutions plays a pivotal role in bridging the gap between innovation and compliance. With extensive expertise in navigating Brazil’s regulatory landscape, Hegemoni offers tailored guidance to ensure seamless integration of advanced technologies like micromotors into the ART sector. From facilitating ANVISA approvals to advising on ethical and operational best practices, Hegemoni empowers innovators to align with Brazil’s legislative requirements while maximizing their market potential.
By fostering collaborations between regulatory bodies, clinicians, and innovators, Brazil is poised to position itself as a global leader in advanced ART technologies. This collaborative effort not only addresses the growing challenges of infertility but also reinforces the nation’s standing as a hub for innovation and ethical excellence. For international companies and researchers, Brazil offers a promising market where cutting-edge advancements can flourish under a well-defined and expertly navigated regulatory framework.